U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market Size and Trends
The U.S. specialty injectable generics market size was exhibited at USD 22.57 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 50.29 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.34% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
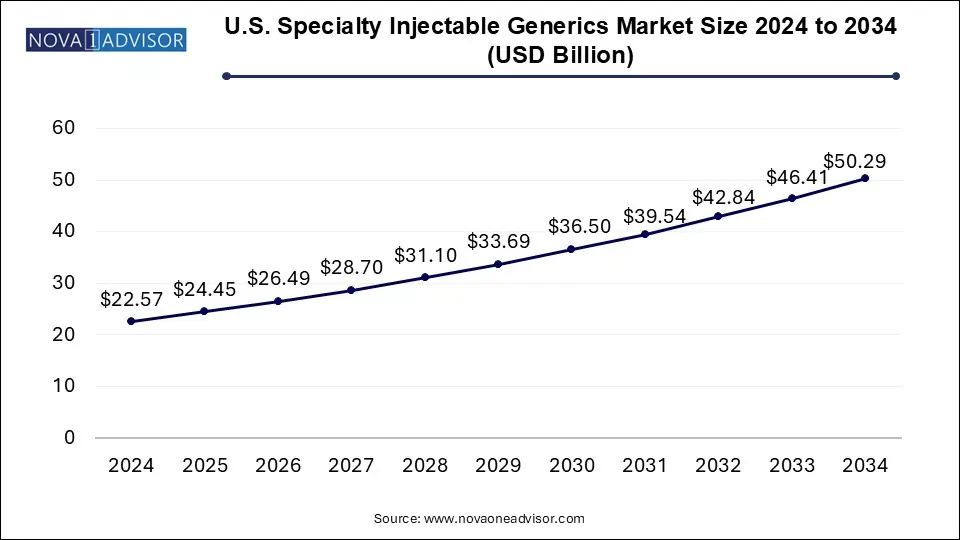
U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market Key Takeaways:
- In 2024, the biologics segment gained a major market share of 60.41% owing to the expected commercialization of biologics.
- Biologics segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 9.5% over the forecast period
- In 2024, the oncology segment held the largest share accounting for about 48.9%.
- On the other side, CNS is expected to show the fastest growth rate over the projected period.
- The hospital segment held the largest share of 57.0% in 2024 and is expected to maintain its position throughout the forecast period.
- However, retail pharmacy is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market represents one of the most dynamic and high-value segments within the broader generic pharmaceuticals industry. Specialty injectable generics refer to non-branded injectable drugs both chemical and biologic that are used to treat complex, chronic, or rare medical conditions. These products are typically administered in clinical settings such as hospitals or infusion centers and include therapies for cancer, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and central nervous system (CNS) disorders.
In contrast to traditional oral generics, specialty injectable generics face greater manufacturing, regulatory, and distribution challenges. These drugs often require advanced formulation techniques, cold-chain logistics, and robust clinical evidence to meet the standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Nevertheless, their market potential has soared in recent years, primarily due to escalating healthcare costs, increased prevalence of chronic diseases, and the expiration of patents for high-cost biologics and specialty injectables.
In the United States, a growing emphasis on cost containment by both public payers like Medicare and private insurers—has fueled the adoption of generic alternatives to specialty brand-name injectables. Hospital systems, group purchasing organizations (GPOs), and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) actively pursue cost-effective generic options to improve patient access and optimize budget allocations. At the same time, the FDA’s support for expedited approvals under the Competitive Generic Therapies (CGT) pathway is accelerating the market entry of complex injectables.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the injectable drug supply chain and prompted significant investment in domestic production. These developments have not only strengthened regulatory momentum but also emphasized the strategic importance of this segment in bolstering public health resilience. With clinical demand and policy support aligned, the U.S. specialty injectable generics market is poised for sustained growth and innovation.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Patent Expirations of Biologic and Specialty Drugs: The loss of exclusivity for blockbuster injectables is creating pathways for generic and biosimilar entrants.
-
Expansion of Biosimilars in Oncology and Autoimmune Care: Biosimilar injectables, especially for monoclonal antibodies, are gaining traction in complex therapeutic areas.
-
Increased FDA Support for Complex Generics: The Competitive Generic Therapies (CGT) and 505(b)(2) pathways are expediting approvals of difficult-to-manufacture injectables.
-
Shift Toward In-House Hospital Compounding and Outsourcing Facilities: Health systems are investing in sterile compounding to mitigate shortages and improve supply reliability.
-
Adoption of Ready-to-Administer (RTA) Formats: Prefilled syringes and RTA vials are improving workflow efficiency in hospitals and reducing medication errors.
-
Supply Chain Localization Post-COVID: Domestic manufacturing initiatives and public-private partnerships are driving U.S.-based production of critical injectables.
-
Private Equity Investment in Sterile Manufacturing Facilities: The market is seeing rising investment in infrastructure and contract development manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) focused on sterile injectables.
Report Scope of U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 24.45 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 50.29 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 8.34% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Application, Distribution Channel |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Pfizer, Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Baxter International, Novartis AG, Fresenius SE & Co. KGaA, Par Pharmaceutical, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, Sagent Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Mylan N.V. |
Key Market Driver: Cost Pressure and Demand for Affordable Alternatives
The leading driver of growth in the U.S. specialty injectable generics market is the relentless cost pressure faced by healthcare providers and payers. Specialty medications account for nearly 50% of total drug spending in the U.S., despite representing less than 2% of prescriptions. Branded injectable drugs particularly biologics are among the most expensive therapies, often costing thousands of dollars per dose.
Generic injectable alternatives, when available, offer significant savings. For example, the introduction of generic alternatives to chemotherapy agents like docetaxel and irinotecan resulted in cost reductions of up to 70% for providers. Biosimilar versions of injectable biologics such as filgrastim (Neupogen) and trastuzumab (Herceptin) have similarly delivered notable cost savings while maintaining clinical efficacy. Hospitals, pharmacy benefit managers, and insurers are increasingly incentivizing the use of these generics to control costs without compromising outcomes.
The financial appeal of specialty generics extends beyond oncology. In therapeutic areas such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis, injectable biosimilars can significantly alleviate payer burden while increasing patient access. This powerful economic incentive continues to propel market growth and diversify the specialty generics portfolio.
Key Market Restraint: Manufacturing Complexity and Supply Disruptions
Despite growing demand, the specialty injectable generics market is constrained by the high complexity and risk associated with sterile manufacturing. Injectable drugs must meet rigorous quality and sterility standards, requiring sophisticated cleanroom environments, aseptic processing, and highly trained personnel. This manufacturing intensity not only drives up costs but also increases the likelihood of supply disruptions due to batch failures or regulatory compliance issues.
Drug shortages remain a persistent problem in the U.S., particularly for critical injectables used in chemotherapy, anesthesia, and infectious disease management. In 2023 alone, the FDA reported significant shortages in more than 100 sterile injectable products, many of which were generics. These shortages disrupt patient care, increase costs for providers, and erode trust in generic drug reliability.
Moreover, limited competition in certain injectable categories can lead to market monopolies or duopolies, increasing price volatility and limiting price savings. Ensuring consistent supply and quality of specialty injectable generics requires long-term investment in robust manufacturing infrastructure, stringent quality assurance, and diversified supply chains—barriers that only a few players can effectively navigate.
Key Market Opportunity: Growth of Biosimilar Injectables
A major growth opportunity within the U.S. specialty injectable generics market lies in the expanding footprint of biosimilar injectables. Biosimilars are biologic products that are highly similar to already-approved reference biologics, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. As numerous biologic drugs lose patent protection, the stage is set for biosimilar manufacturers to enter the market with injectable products targeting conditions such as cancer, inflammatory diseases, and anemia.
The FDA has approved more than 40 biosimilars to date, with many targeting high-cost injectable biologics like adalimumab (Humira), bevacizumab (Avastin), and epoetin alfa (Epogen). These biosimilars not only offer price competition but also create options for subcutaneous or intravenous administration, increasing clinician and patient flexibility.
Payers are increasingly encouraging biosimilar uptake through tiered formulary structures and outcome-based reimbursement models. Meanwhile, pharmaceutical companies are investing in educational campaigns to boost physician confidence and mitigate biosimilar skepticism. With the biosimilar pipeline growing rapidly and policy support from the FDA and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), this segment offers robust, long-term potential for market players.
U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market By Type Insights
Drugs currently dominate the specialty injectable generics market in the U.S., driven by high-volume products used in oncology, anesthesia, and critical care. These include generic versions of chemotherapy agents, anesthetics like propofol, antibiotics such as vancomycin, and anticoagulants like enoxaparin. The maturity of this segment has allowed for a stable supply chain, with key manufacturers offering competitive pricing and therapeutic interchangeability. Hospitals and infusion centers routinely rely on these generic injectables for standardized care pathways, contributing to steady demand.
However, biologics are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, propelled by biosimilar developments and the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions requiring biologic therapy. Injectable biosimilars for cancer, autoimmune diseases, and growth disorders are witnessing accelerated approvals and commercial uptake. Products such as biosimilar trastuzumab and pegfilgrastim have demonstrated strong clinical acceptance and growing formulary inclusion. The rise of CDMOs with biologics manufacturing capabilities, combined with evolving regulatory support, will likely further strengthen this segment in the coming years.
U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market By Application Insights
Oncology is the dominant application for specialty injectable generics, accounting for a substantial share of drug volumes and revenues. Cancer treatments often rely on complex injectable regimens, including chemotherapy agents, supportive care drugs (e.g., antiemetics, hematopoietic agents), and targeted therapies. The availability of generic doxorubicin, carboplatin, and paclitaxel has transformed cancer care affordability. Biosimilars for monoclonal antibodies such as rituximab and bevacizumab have also gained traction in treating lymphoma and colorectal cancer, respectively.
Autoimmune disorders are the fastest-growing application area, due to rising prevalence and increasing use of biologic therapies. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis are being managed through injectable biosimilars of adalimumab and etanercept, offering a cost-effective alternative to branded biologics. Specialty pharmacies and hospital outpatient departments are expanding their capabilities to handle these complex biologic injections, particularly as patients seek home-based care options. This segment is expected to see sustained growth through the expansion of indications, new biosimilar launches, and broader insurance coverage.
U.S. Specialty Injectable Generics Market By Distribution Channel Insights
Hospitals remain the dominant distribution channel for specialty injectable generics, especially for acute treatments and infused therapies. Inpatient and outpatient hospital settings manage a wide range of injectable therapies—from pre-operative drugs and anti-infectives to chemotherapy infusions. Hospital pharmacy departments maintain close relationships with GPOs and manufacturers to ensure volume discounts and secure supply. Furthermore, the emergence of 503B outsourcing facilities has supported hospitals in sourcing sterile compounded injectables during shortages.
Retail pharmacies are the fastest-growing distribution channel, spurred by the integration of specialty pharmacies and increased patient access to biologics and biosimilars. Large pharmacy chains such as CVS and Walgreens, along with online platforms like Amazon Pharmacy, are investing in infrastructure to manage cold-chain, injectable therapies. With regulatory shifts allowing more injectable biosimilars to be administered outside the clinical setting, retail pharmacies are poised to expand their role in dispensing and administering specialty injectables, particularly in chronic disease management and de-addiction therapy.
Country-Level Analysis
The United States dominates the global specialty injectable generics market, with a unique combination of clinical demand, regulatory pathways, and healthcare complexity. The U.S. healthcare system incentivizes generics to manage soaring drug expenditures, making it a fertile ground for specialty generic adoption. The FDA’s approval of complex generics and biosimilars is accelerating, with multiple guidance documents issued to assist developers of injectables such as liposomal formulations and depot injections.
Healthcare providers are under mounting pressure to reduce costs while maintaining high-quality care. Specialty injectable generics address this dual need by offering therapeutic parity at reduced costs. The U.S. market also benefits from the presence of a mature contract manufacturing ecosystem, led by players like Baxter, Catalent, and Pfizer CentreOne, supporting the supply of high-quality injectables across hospitals and specialty pharmacies.
At the same time, the U.S. faces challenges including price volatility, supplier consolidation, and regulatory scrutiny following quality lapses. The government is investing in public-private partnerships to enhance domestic production of critical injectables, while also supporting transparency in drug pricing and patient access. The future of the market will be shaped by how well stakeholders can balance innovation, cost, and supply integrity.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. specialty injectable generics market include:
Recent Developments
-
In March 2025, Amneal Pharmaceuticals launched a biosimilar version of pegfilgrastim in the U.S. market, targeting supportive oncology care.
-
In February 2025, the FDA approved a generic liposomal bupivacaine developed by Pacira BioSciences, marking a major milestone in complex generic approvals.
-
In January 2025, Pfizer announced a $750 million investment to expand its sterile injectable manufacturing facility in Kalamazoo, Michigan, as part of its domestic supply chain strategy.
-
In December 2024, Civica Rx, a nonprofit generic drug company, entered into an agreement with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to supply essential injectable drugs to the national stockpile.
-
In November 2024, Teva Pharmaceuticals launched an interchangeable biosimilar for trastuzumab, expanding its oncology injectables portfolio across hospital systems.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. specialty injectable generics market
By Type
By Application
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular
- CNS
- Infectious Diseases
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospitals
- Retail Pharmacy
- Others

